
Optical Lens-Infrared Lens
2021-09-08
Optical Lens-Infrared Lens
Introduction
What do you expect most when you are in the dark? Of course it is a pair of eyes that can see through the dark, and an infrared lens is this kind of eyes that can perceive heat and see through the dark.
Part One——Infrared Light
Light is an electromagnetic wave, classified from low to high frequency, including radio waves, microwaves, infrared rays, visible light, ultraviolet rays, X-rays, gamma rays, and radio. As shown in the figure below, only the electromagnetic waves in the visible spectral range of 0.38-0.76um are visible to the human eye, while the electromagnetic waves in the infrared spectral range of 0.76-1000um are invisible to the human eye.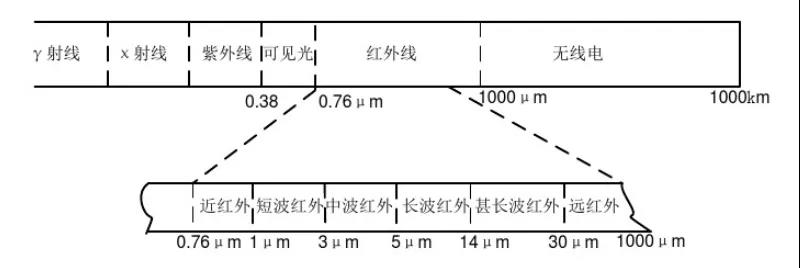
The part of infrared light of 0.78-3.0μm is infrared; the part of infrared light or thermal infrared of 3.0-18μm, as long as it is a real object with absolute zero temperature, it can emit electromagnetic waves. Other objects at extremely zero degrees, so when the light is irradiated, they are surrounded by thermal infrared rays. Infrared (or thermal radiation) exists as a thermal target and has important characteristics:
1) The magnitude of the thermal radiation energy of this kind of object is related to the ground temperature. People can use it to perform non-contact temperature testing and thermal state analysis of the object, thereby providing an important testing capital for industrial production, energy, environmental protection, etc. And diagnostic tools.
2) The atmosphere, smoke, etc. absorb visible light and near-infrared rays, but are transparent to thermal infrared rays of 3-5μm and 8-14μm. Therefore, using these two images, you can clearly observe the surrounding situation when you look at the battlefield in a completely dark hidden place and against the backdrop of dense clouds.
Part Two——Infrared thermal imaging technology
Infrared thermal imaging is passive imaging, which turns the terrain that the human eye can't see into the thermal image of the terrain and landform radiation that the human eye sees. Temperature emits images; different objects and surrounding objects have different suction powers, which use different light from the object and the environment and various objects of the object. Thermal infrared can display various objects of the object, so that the object can be displayed. Characteristics.

Infrared thermal imaging cameras can be divided into two types: refrigerated and uncooled according to their working temperature.
1) Cooled type: a low temperature cooler is integrated in the detector to cool the detector. In order to make the thermal noise signal lower than the imaging signal, the imaging quality is better.
2) Uncooled type: The detector does not require low temperature cooling, usually a microbolometer, suitable for working in an environment close to room temperature.

Part Three——Infrared Lens
Infrared thermal imaging lens is also a kind of optical lens. The infrared light emitted by the lens group converges to the image sensor (chip), and the photoelectric signal is converted by the chip. The final formation is composed of the thermal infrared difference between the object itself and the background. Thermal infrared image. In order to reduce the influence of the background noise signal, the smaller the F number, the better; in the case of extreme cold, extreme heat, or large temperature differences, the curvature, thickness, refractive index and lens barrel changes of the infrared lens will cause the lens to defocus In order to ensure clear imaging, the lens needs to be refocused, electric or manual focusing is required, to eliminate the adverse effects of temperature changes, an athermal design is required, and different optical materials are usually used for optical compensation (temperature difference), or The design of mechanical materials and optical materials with opposite trends is adopted for opto-mechanical compensation.
The most commonly used infrared lens is germanium crystal with a refractive index of 4.0, which is suitable for the 2-25μm band; while the silicon crystal with a refractive index of 3.0 is often used in the 1-6um band. Infrared crystal materials such as silicon germanium have limited raw materials and are expensive, so aspheric or diffractive surfaces are usually used in many optical system designs to reduce the number of lenses while taking into account excellent imaging effects. With the popularization of commercial infrared applications, such as night vision, rifle sights, vehicles, etc., chalcogenide glass is also suitable for mass production due to its low raw material cost, high processing efficiency, and good temperature stability.
Infrared thermal imaging lenses can generally be divided into two categories: medium-wave infrared thermal imaging lenses (MWIR lenses) and long-wave infrared thermal imaging lenses (LWIR lenses) according to the wavelength application window.
1) MWIR lens is suitable for scenes with high object temperature. Its working wavelength mainly falls in the mid-wave infrared of 3.0-5.0μm. It has strong ability to penetrate smoke and dust, high resolution, and excellent image quality; usually in cooperation The wave-cooled detector is used, the diaphragm is placed behind the lens, so the lens and the camera are bulky, but the detection distance is very long, such as a lens with a focal length of 150mm and 300mm, which can see a distance of 10 km-30 km; at the same time, it is concealed Well, the feature of being able to work day and night is widely used in military and high temperature measurement fields.
2) LWIR lens is suitable for scenes where the object temperature is low. Its working wavelength mainly falls on the long-wave infrared of 8.0-14μm. The resolution is low, but it can provide high-precision temperature measurement; it is usually used with long-wave uncooled detectors. , Its lens design is commercial-oriented, low-cost, light and compact, and easy to maintain. It is widely used in electric power, chemical, fire, medical and other fields.
Copyright © 2020 Foctek Photonics, Inc. All Rights Reserved All Rights Reserved 闽ICP备05011100号
Power:BAINANET

 sales@foctek.com
sales@foctek.com